Toolkit
1. Introduction
The Toolkit module is one of the core components of Chat2Graph. Its primary responsibility is to recommend specific execution instructions and provide capabilities for interacting with the external world to the framework's Operator. It achieves this by meticulously managing a directed graph—the Toolkit—composed of "Actions", "Tools", and "ToolGroups". This graph not only defines the invocation relationships between different tools but also specifies their potential execution sequences, thereby expanding the operational capabilities of the Operator.
This module is dedicated to solving the challenges of tool invocation. It implements an advanced tool management mechanism: a directed graph of Actions, Tools, and ToolGroups that clearly describes the dependencies and transition relationships between tool calls, a significant improvement over a simple, traditional list of tools. Based on this graph structure, the system can more intelligently recommend contextually relevant tools and "Actions" to the Large Language Model (LLM), significantly improving recommendation accuracy. At the same time, the precision of the graph effectively constrains the LLM's tool selection, reducing uncertainty and the potential for errors. For developers, the Toolkit provides a unified mechanism for tool registration and recommendation, allowing Tool and Action objects to be easily reused, thus simplifying the development process. Furthermore, the module already supports the Model Context Protocol (MCP), and future enhancements will include offline learning capabilities to augment the ToolkitService's recommendation abilities through reinforcement learning.
The main features of the Toolkit module include:
- Support for defining and registering Tools and ToolGroups, compatible with the LLM's function-calling paradigm.
- The ability to define Actions, where each action can contain a set of available tools and links to subsequent possible actions.
- The core
Toolkitcomponent, which is responsible for the overall construction and management of the tool graph. - These functionalities are managed as a service through the
ToolkitServiceand exposed via a convenient SDK interface, theToolkitWrapper, for upper-layer applications.
The Toolkit is shared across the entire system, making its Actions and Tools reusable.
2. Design
2.1. Tool Graph Design
Toolkit organizes tools and actions using a directed graph structure. The primary nodes in the graph are Action nodes, each of which can be associated with a set of Tool nodes, representing the operations executable under that Action. Additionally, an Action points to subsequent possible Action nodes via its next_action_ids attribute. In the Toolkit graph, Action nodes are connected by weighted Next edges, indicating the sequential relationship and strength of association between actions. Action nodes are connected to their associated Tool nodes by weighted Call edges, representing the logical relationship and likelihood of the action invoking the tool. ToolGroup nodes serve as logical collections of Tools and are connected to each of their contained Tools via a Group_Has_Tool edge (with a fixed weight of 1), denoting an ownership relationship for easier management.
-
Tool: Represents a single, executable tool. Each tool includes its name, a description of its functionality, a JSON Schema definition of its input parameters, and its execution logic. In the Toolkit, aToolis the basic execution unit invoked by anAction. Tools can be called by theReasoner. Furthermore, the Toolkit supports dependency injection for services defined inapp.core.reasoner.injection_mapping(e.g.,GraphDbService), automatically providing them as parameters during tool invocation. This means you do not need to declare service module parameters in the docstring, as theReasonerwill automatically detect and inject the corresponding module, enhancing the tool's flexibility and power. -
Action: Represents a state or decision point for the LLM during task execution and is a core node in theToolkitgraph. The description of anActionhelps the LLM understand its intent and function. AnActioncan be associated with one or moreTools, indicating that these tools might be called when executing thisAction. -
ToolGroup: A logical collection ofTools, typically representing an internal or external service (like an MCP server) or a set of functionally related tools. This facilitates the bulk registration and management of tools. -
Toolkit: Responsible for organizing and managing the directed graph composed of multipleAction,Tool, andToolGroupnodes. It is more than a simple collection of tools; it clearly expresses the invocation logic, organizational structure, and workflow of tasks. -
ToolkitService: Manages theToolkitinstance and recommends appropriateActions andTools to the LLM based on the current context.
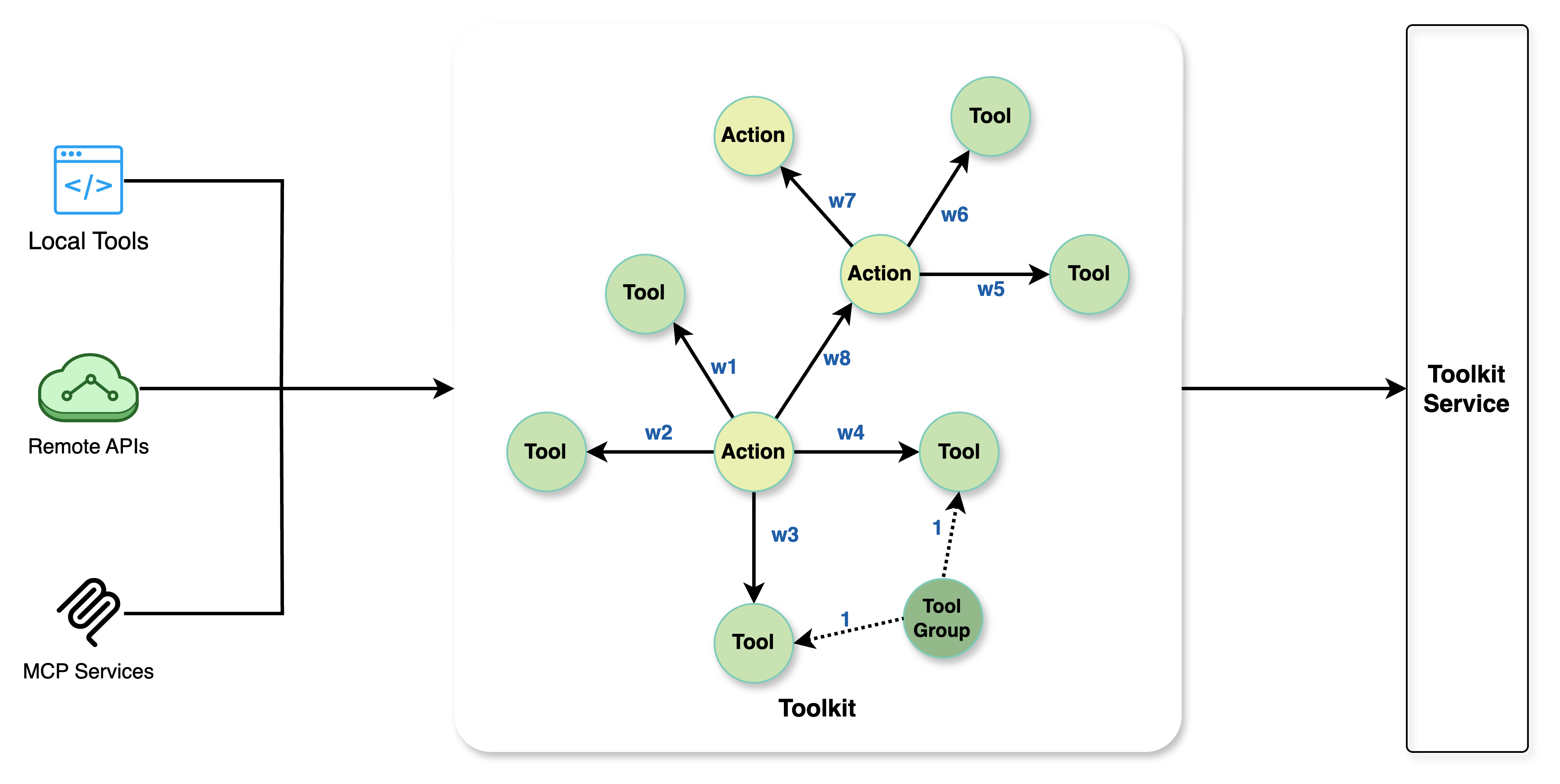
This graph-based Toolkit mechanism offers significant advantages. First, it enables context-aware tool recommendation: the system can more accurately recommend available Tools or the next possible Action based on the current Action node's position in the graph, which is far more intelligent and efficient than providing a flat, context-free list of tools. Second, the predefined graph structure effectively narrows the search space for the LLM when selecting tools or deciding on the next step, significantly reducing randomness and uncertainty, thereby improving the accuracy of tool calls and the overall efficiency of task execution. Finally, this structured approach makes modeling complex processes more natural and intuitive, allowing for the clear representation of multi-step, dependent, or conditional tool invocation flows.
2.2. Toolkit Implementation
-
Initial Configuration: The system predefines sets of
Actions,Tools, andToolGroups, as well as theActions bound to anOperator, via YAML configuration. Tools for graph database operations are integrated as a built-in capability and can be registered simply through the Graph Database service. Dynamic tool registration capabilities are currently under development. -
Tool Recommendation: Based on the set of
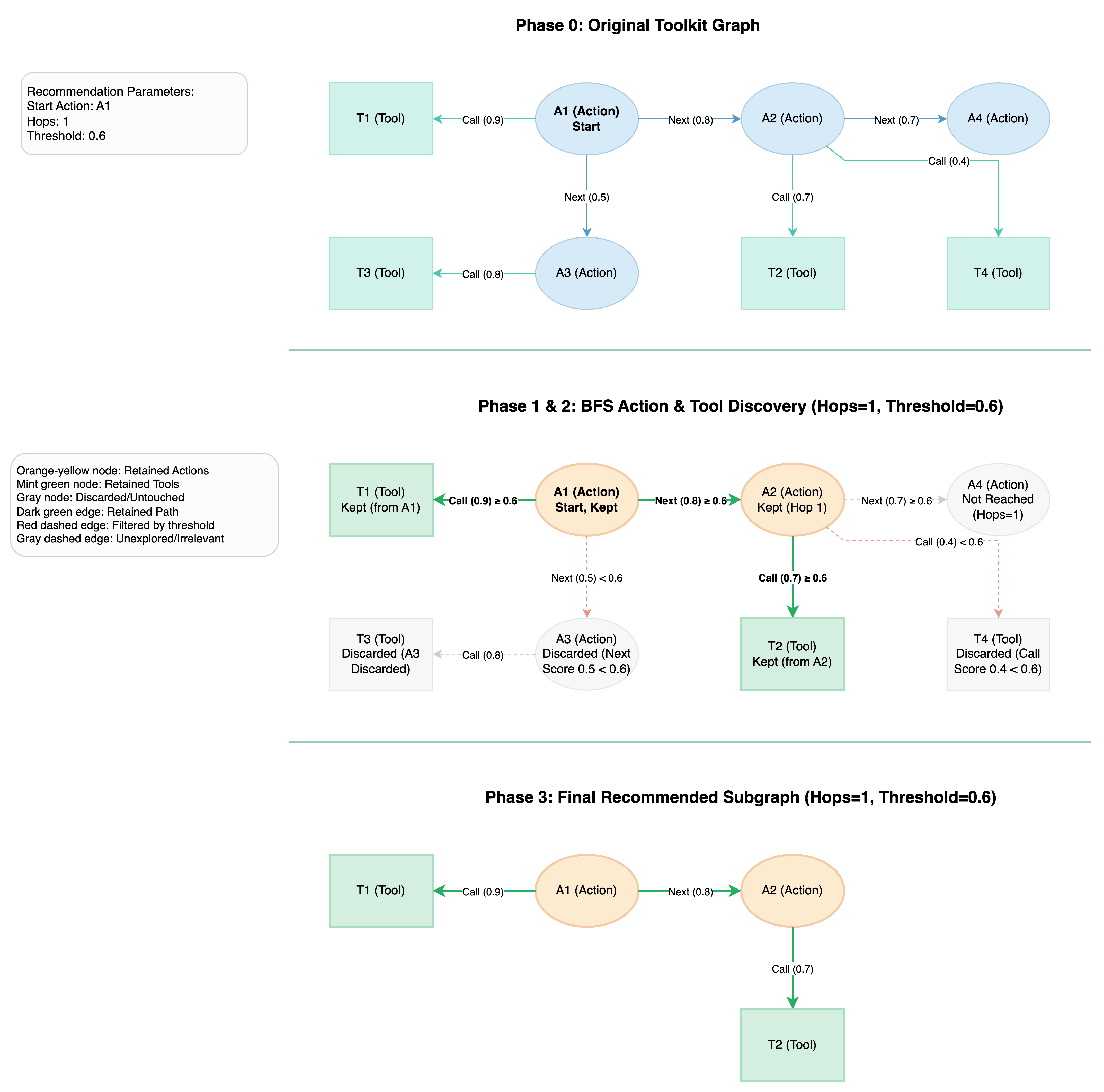
Actions bound to anOperator, theToolkitServiceperforms a graph traversal within the Toolkit. It finds otherActions and availableTools associated with the currentActionand provides them as recommendations. The scope of these recommendations (e.g., traversal depth or association strength) can be controlled by configuring thresholds and the number of hops for the graph traversal.
- Tool Invocation: The
Reasoner(often combined with the LLM's decision-making capabilities) selects the most appropriateToolfrom the list ofActions andTools recommended by theToolkitService. Once selected, theReasonerexecutes theTooland uses its result for subsequent task processing.

- Toolkit Enhancement: The Toolkit's capabilities are continuously being optimized, with planned features such as one-click registration for toolsets and enhancements to the tool graph based on reinforcement learning.

2.3. API
2.3.1. Toolkit API
The Toolkit class inherits from Graph and is specifically designed to build and manage the directed graph of Actions, Tools, and ToolGroups.
| Method Signature | Description |
|---|---|
add_vertex(self, id, **properties) -> None | Adds a vertex (Action, Tool, or ToolGroup) to the graph. The properties dictionary should contain a data key with the corresponding object as its value. The object is stored in the appropriate internal dictionary based on its type. |
vertices_data(self) -> List[Tuple[str, Dict[str, Union[Action, Tool, ToolGroup]]]] | Retrieves all vertices and their associated data from the toolkit. Returns a list of tuples, where each tuple contains a vertex ID and a dictionary with its data. |
update(self, other: Graph) -> None | Updates the current graph with vertices and edges from another Toolkit instance (other). New Actions, Tools, ToolGroups, or edges and their scores are added, while existing ones are not duplicated. |
subgraph(self, ids: List[str]) -> "Toolkit" | Creates and returns a new Toolkit instance that is a subgraph of the original, containing only the specified vertex IDs and the edges between them. |
remove_vertex(self, id: str) -> None | Removes a vertex from the graph, triggering a one-way cascading delete: 1. Deleting an Action removes any Tool that becomes orphaned (i.e., has no other Action connected to it). 2. Deleting a ToolGroup removes all Tools it contains. 3. Deleting a Tool will also remove its parent ToolGroup if that ToolGroup is only connected to that single Tool. |
get_action(self, id: str) -> Optional[Action] | Retrieves the Action object associated with a vertex ID. Returns None if the ID does not exist or does not correspond to an Action. |
get_tool(self, id: str) -> Optional[Tool] | Retrieves the Tool object associated with a vertex ID. Returns None if the ID does not exist or does not correspond to a Tool. |
get_tool_group(self, id: str) -> Optional[ToolGroup] | Retrieves the ToolGroup object associated with a vertex ID. Returns None if the ID does not exist or does not correspond to a ToolGroup. |
get_score(self, u: str, v: str) -> float | Gets the score of the edge connecting vertices u and v. Defaults to 1.0 if the edge does not exist. |
set_score(self, u: str, v: str, score: float) -> None | Sets the score for the edge connecting vertices u and v. |
2.3.2. Toolkit Service API
ToolkitService is a singleton service that manages the Toolkit instance and provides functionalities for tool and action registration, recommendation, and visualization.
| Method Signature | Description |
|---|---|
get_toolkit(self) -> Toolkit | Returns the Toolkit instance currently managed by the service. |
add_tool(self, tool: Tool, connected_actions: List[Tuple[Action, float]]) | Adds a Tool to the toolkit. tool is the tool object, and connected_actions is a list of Action objects that call this tool, along with their corresponding scores. A warning is printed if an Action is not in the graph or if the tool has no connecting Actions (in which case the tool is removed). |
add_tool_group(self, tool_group: ToolGroup, connected_actions: List[Tuple[Action, float]]) -> None | Adds a ToolGroup and all of its contained tools. tool_group is the tool group object, and connected_actions is the list of Actions that call these tools, along with their scores. This method registers the ToolGroup node, then adds all its tools, creating both ToolGroup->Tool and Action->Tool connections. |
add_action(self, action: Action, next_actions: List[Tuple[Action, float]], prev_actions: List[Tuple[Action, float]]) -> None | Adds an Action to the toolkit. action is the action object, while next_actions and prev_actions are lists of its subsequent and preceding Actions, respectively, along with their association scores. |
get_action(self, action_id: str) -> Action | Retrieves an Action object from the toolkit by its action_id. Throws a ValueError if not found. |
remove_tool(self, tool_id: str) | Removes a Tool from the toolkit by its tool_id. |
remove_action(self, action_id: str) | Removes an Action from the toolkit by its action_id. |
recommend_subgraph(self, actions: List[Action], threshold: float = 0.5, hops: int = 0) -> Toolkit | The core recommendation method. Based on a list of input Actions, it performs a weighted Breadth-First Search (BFS) within a specified number of hops to find related Actions and their associated Tools. Only relationships with scores greater than or equal to the threshold are included. Returns a Toolkit subgraph. |
recommend_tools_actions(self, actions: List[Action], threshold: float = 0.5, hops: int = 0) -> Tuple[List[Tool], List[Action]] | Based on the result of recommend_subgraph, this method extracts the Tools and Actions from the recommended subgraph and returns them as a tuple of lists. |
visualize(self, graph: Toolkit, title: str, show=False) | Visualizes the given Toolkit graph. Action, Tool, and ToolGroup nodes are displayed with different colors and shapes. Edges are also styled by type and labeled with their scores. title is the chart title, and show determines whether to display the image immediately. Returns a matplotlib.pyplot.Figure object. |
3. Examples
- Registering
Actions,Tools, andToolGroups with theToolkit:test/example/run_toolkit.py - Recommending
Actions andTools to anOperatorviaToolkitService:test/example/run_operator.py - Integrating with a browser MCP:
test/example/mcp/run_playwright_mcp.py - Integrating with a local file system MCP:
test/example/mcp/run_file_system_mcp.py